Artificial Intelligence & Machine Language
June 3, 2021
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
June 29, 2021Cloud vs. Edge Computing: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Is edge computing just new branding for a type of cloud computing, or is it something truly new? Let’s examine how the edge approach works, where edge makes sense, and how edge and cloud will coexist..
Doing enterprise computing in the cloud is no longer a novel concept. But what about the edge? You’re hearing more about edge computing, often in the same breath as talk about 5G and Internet of Things (IoT). So is edge computing just new branding for a type of cloud computing, or is it something truly new? As is often true on the frontiers of technology, there is room for debate about the answers to these questions and the precise definition of what does and does not qualify as edge computing.
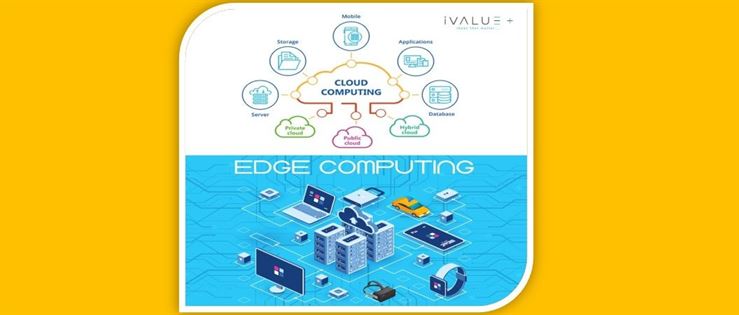
What is Cloud Computing?
In a cloud computing architecture, all data is gathered and processed in a centralized location, usually in a data center. All devices that need to access this data or use applications associated with it must first connect to the cloud. Since everything is centralized, the cloud is generally easy to secure and control while still allowing for reliable remote access.
Public cloud services such as Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, and Google Cloud provide tremendous benefits for organizations that use a traditional client/server network. By storing assets and information in a centralized cloud, they ensure that authorized users can access the information and tools they need from anywhere at any time.
Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing
While the cloud revolutionized the way we handle data and the way businesses were able to provide applications and services to their customers, it comes with limitations as well.
First, the centralized nature of cloud computing makes it difficult to process data gathered from the edge of the network quickly and effectively. What the cloud lacks in speed, however, it makes up for in power and capacity. Since cloud computing is based upon a scalable data center infrastructure, it can expand its storage and processing capacity as needed. This scalability is a huge benefit for small businesses looking to expand quickly.
Cloud computing allows for a level of large scale data analysis that simply isn’t possible at the edge of the network. With its unparalleled storage and processing potential, the cloud can gather massive amounts of data and analyze it in a variety of ways to produce valuable insights, trends, and solutions. The data analysis capabilities of cloud computing have even allowed artificial intelligence and machine learning to become more viable.
Cloud computing will continue to be a valuable resource for more traditional data center infrastructures. While IoT devices represent an exciting new frontier in the tech industry, not all businesses will see much benefit from moving their assets to the edge of the network. The various “as a service” providers, for instance, can provide better service and security by hosting their products in a centralized cloud.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing harnesses the concept of the cloud, in that the servers connect to the user via the internet, but it shifts the servers closer to the end user. The “edge” in this case, refers to the edges of high density population centers and the “edges” of networks, the outer periphery of both.
Pros and Cons of Edge Computing
As Internet of Things (IoT) devices become more common and incorporate more processing power, a vast amount of data is being generated on the outer “edge” of computing networks. Traditionally, the data produced by IoT devices is relayed back to a central network server, usually housed in a data center. Once that data is processed, further instructions are sent back to the devices out on the edge of the network. However, this more traditional setup creates a lot of issues with speed and latency.
Edge computing offers a solution to the latency problem by relocating crucial data processing to the edge of the network. Rather than constantly delivering data back to a central server, edge enabled devices can gather and process data in real time, allowing them to respond faster and more effectively. When used in tandem with edge data centers, edge computing is a versatile approach to network infrastructure that takes advantage of the abundant processing power afforded by the combination of modern IoT devices and edge data centers. However, one major limitation of edge devices is that they only accumulate locally collected data, it is difficult for them to utilize any kind of “big data” analytics.
As more and more content providers get into the streaming business, it can be difficult for network infrastructure to keep up with consumer demands. Edge caching, which allows content providers like Netflix and Amazon Prime to cache popular content in edge facilities located closer to end users for quick and speedy access, will help these companies to expand services without compromising their current performance.
Edge Computing Vs. Cloud Computing – Which One’s Better?
First, it’s important to understand that cloud and edge computing are different, non-interchangeable technologies that cannot replace one another. Edge computing is used to process time-sensitive data, while cloud computing is used to process data that is not time-driven.
Besides latency, edge computing is preferred over cloud computing in remote locations, where there is limited or no connectivity to a centralized location. These locations require local storage, similar to a mini data center, with edge computing providing the perfect solution for it.
Edge computing is also beneficial to specialize and intelligent devices. While these devices are akin to PCs, they are not regular computing devices designed to perform multiple functions. These specialized computing devices are intelligent and respond to particular machines in a specific way. However, this specialization becomes a drawback for edge computing in certain industries that require immediate responses. That was all about edge computing vs. cloud computing. Moving forward, let us discuss the future of these platforms in detail.